Consumers
In this document, you will learn the basic concepts of consumers in API7 Enterprise and why you need them. You will be introduced to a few relevant concepts, including how to pass consumer information to upstream, consumer access restriction, as well as consumer authentication and authorization.
Overview
A consumer represents a user, application, or host that sends requests to the API gateway and consumes backend services. It is used together with the authentication system. Each consumer must be configured with at least one authentication credential or integrated with an external authentication system using plugins like Authz-Keycloak or OpenID Connect.
The following diagram illustrates an example of API7 Enterprise with one route and two consumers. One consumer, FetchBot, is a data fetching bot, and the other consumer, JohnDoe, is a user. The route and consumers are enabled with the key-auth plugin. Therefore, requests will be authenticated with API keys. To access the internal service, FetchBot sends its requests with bot-key and JohnDoe sends his request with john-key.
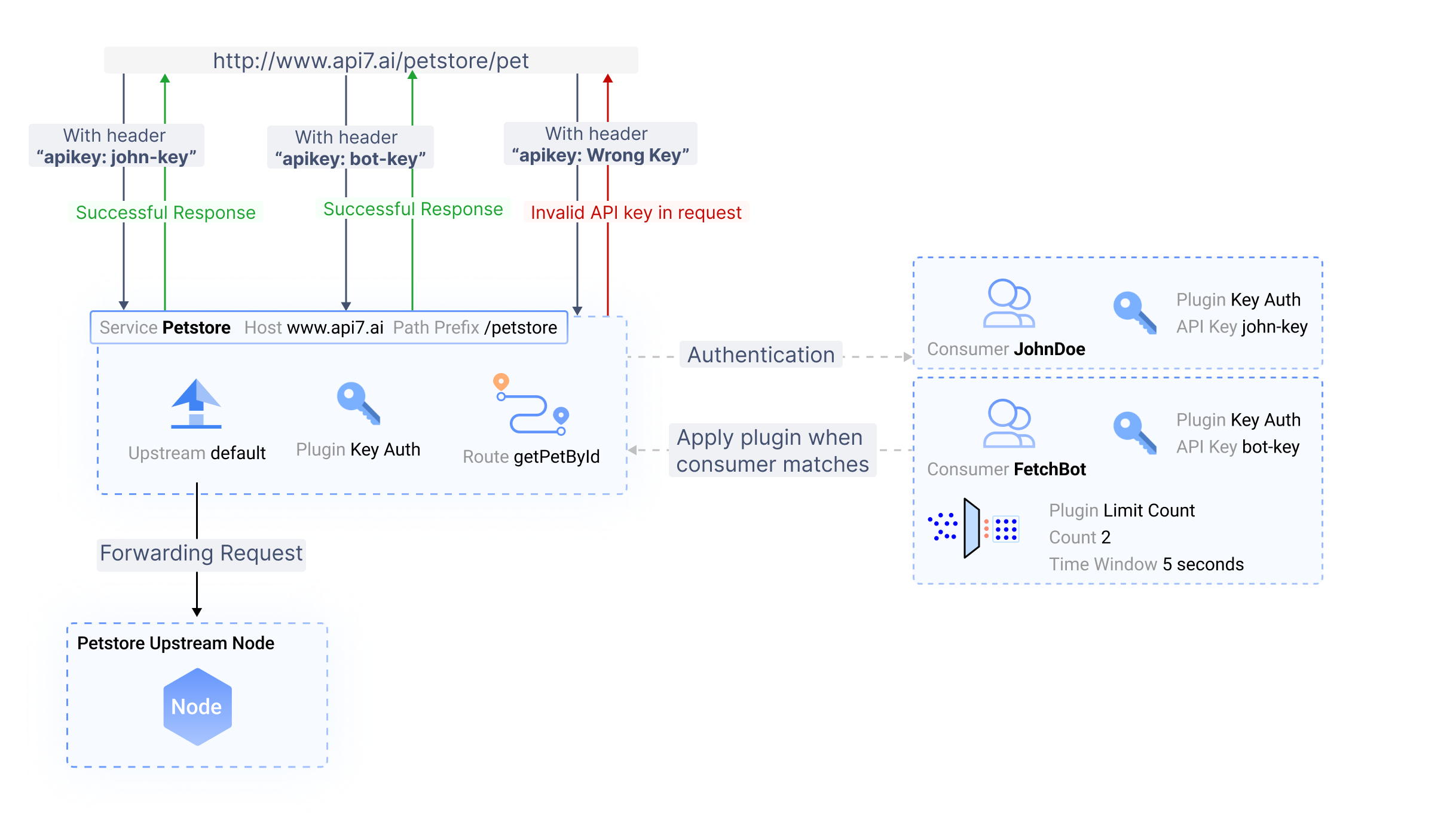
This configuration ensures that only authenticated requests can interact with the internal service exposed on /petstore.
- If a request is sent to API7 Enterprise without any key or with the wrong key, the request is rejected.
- If a request is sent to API7 Enterprise with
bot-key, the request is authenticated and sent byFetchBotto fetch data from the internal service. Thelimit-countrate limiting plugin on theFetchBotconsumer takes effect, limiting the number of requests within a 5-second window to2. If the rate-limiting threshold has not been met, the request is forwarded to the upstream service. Otherwise, it is rejected. - If a request is sent to API7 Enterprise with
john-key, the request is authenticated and sent byJohnDoe, subsequently being forwarded to the upstream endpoint.
In this scenario, the authentication plugin is executed before the limit-count rate limiting plugin in accordance with the plugins execution phases.
Consumer Authentication & Authorization
There are two main design patterns for building authentication and authorization in an API7 Enterprise-based architecture.
The first and most commonly adopted approach is to authenticate and authorize requests through a third-party identity provider (IdP), such as Keycloak:
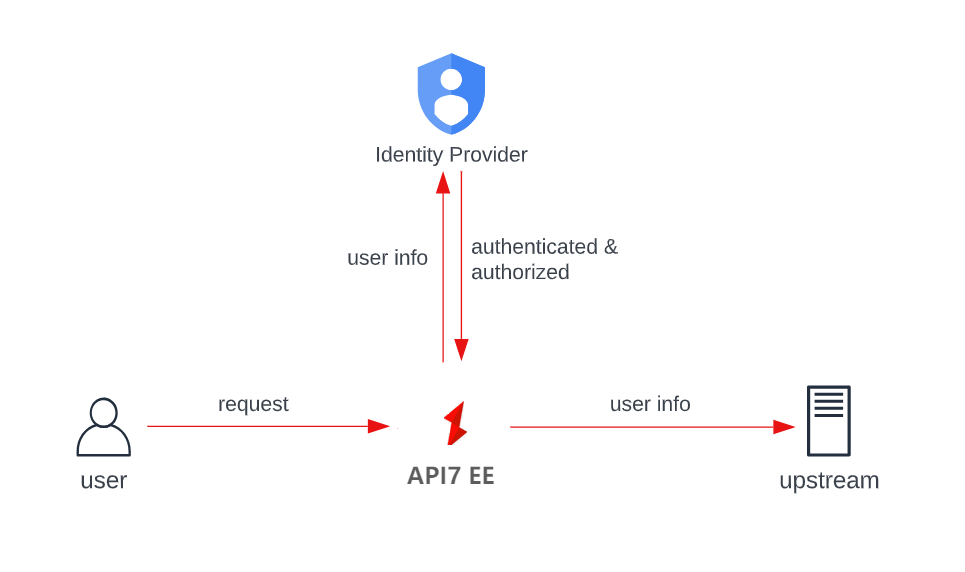
In some environments, a request might need to go through more than one IdP before it can be forwarded to the upstream endpoints. In such cases, you can configure multiple authentication plugins, each corresponding to an IdP on one consumer. API7 Enterprise will not show a successful response until all IdPs have granted access to the request.
The second and more basic approach is to perform authentication and authorization on the API gateway itself, using built-in credentials. So far credentials contains Key Authentication, Basic Authentication, JWT Authentication, and HMAC Authentication.
Similar to traditional user logins, each consumer can create multiple credentials, all linked to a single consumer identity. Credentials should be securely stored and regularly updated.
Consumer credentials offer enhanced flexibility by allowing multiple credentials per consumer. They replace traditional authentication plugins like key-auth, basic-auth, JWT-auth, and HMAC-auth, providing a more user-friendly experience.
Additional Resources
- API Security
- API Consumption